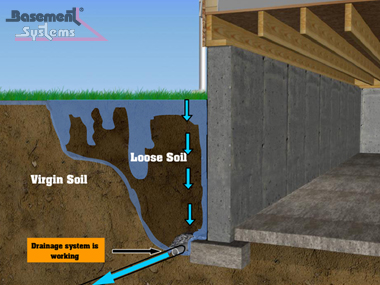
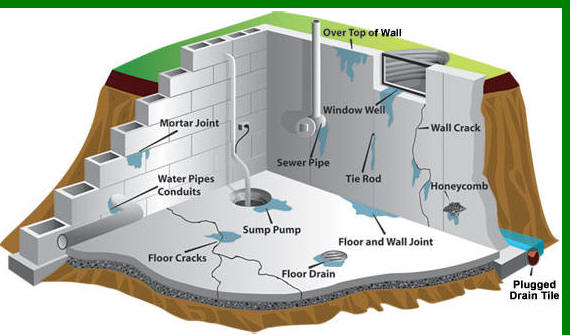
Basement floor cracks that seep water often indicate underlying structural or drainage issues. These cracks typically form due to concrete shrinkage during curing, settling of the foundation, or hydrostatic pressure from saturated soil. Hairline cracks may only leak during heavy rains, while larger gaps can allow constant moisture intrusion. Identifying the crack pattern helps determine the cause—straight cracks often result from shrinkage, while jagged fractures may signal foundation movement. Water seepage through these openings leads to mold growth, damaged belongings, and potential structural deterioration if left unaddressed. Addressing the problem promptly prevents more extensive repairs later.
Effective repair begins with proper crack preparation. Clean the crack thoroughly using a wire brush and vacuum to remove loose debris and dirt. For active leaks, wait for dry conditions or use a quick-setting hydraulic cement to stop water flow temporarily. Epoxy injection systems provide durable repairs for structural cracks, bonding the concrete back together. Polyurethane foam injections expand to fill cracks and create a flexible, watertight seal. For non-structural cracks, silicone-based caulks or masonry sealants offer simpler solutions. Always follow product instructions regarding surface moisture levels and temperature requirements during application.
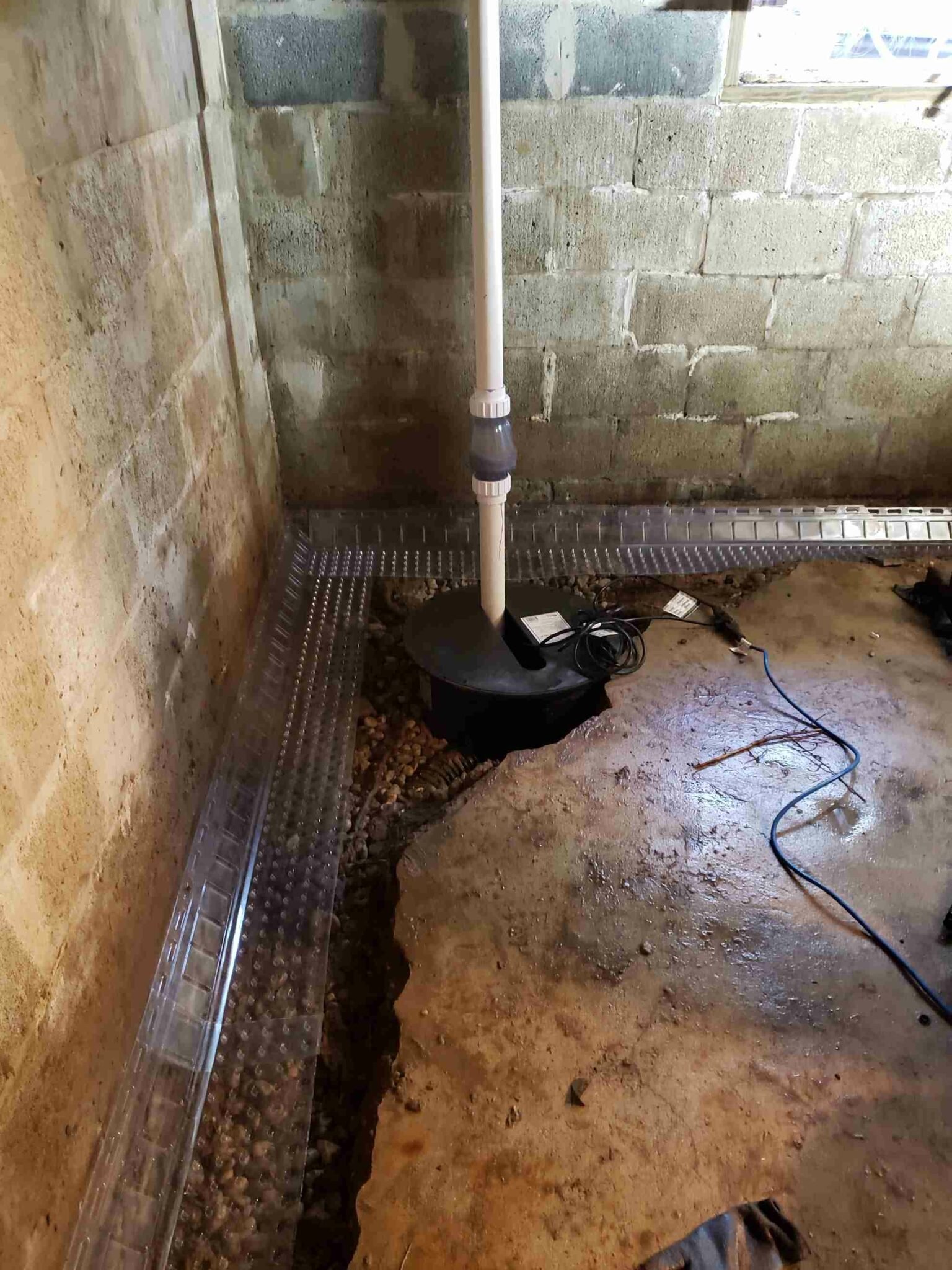
Exterior waterproofing measures complement crack repairs. Improper yard grading often directs water toward foundation walls, increasing hydrostatic pressure. Extending downspouts at least 5 feet from the foundation prevents water accumulation near basement walls. Installing French drains or curtain drains redirects groundwater away from the structure. Exterior waterproofing membranes applied to foundation walls block water penetration at its source. These solutions work best when combined with interior crack repairs to create a comprehensive moisture barrier. A sump pump system may be necessary for basements in high water table areas.
Preventive measures reduce future cracking risks. Control joint installation in new concrete floors allows for natural expansion and contraction. Maintaining consistent indoor humidity levels minimizes concrete shrinkage. Proper compaction of subsoil before pouring basement slabs prevents settling. Waterproofing additives in new concrete mixes enhance resistance to moisture penetration. For existing basements, dehumidifiers help manage ambient moisture that could exacerbate crack formation. Regular inspections after heavy rainfall or seasonal changes catch new cracks early, when repairs are simplest and most effective.
Professional assessment ensures proper long-term solutions. Structural engineers can determine whether cracks indicate serious foundation problems requiring underpinning or piering. Waterproofing specialists use infrared cameras and moisture meters to identify hidden leaks. Advanced solutions like interior drainage systems or epoxy injections may require professional equipment and expertise. While DIY repairs work for minor cracks, persistent or widening gaps warrant expert evaluation. Addressing both the symptoms (cracks) and causes (water pressure) creates a dry, stable basement environment. Proper repairs protect your home’s value and prevent health hazards from mold and mildew growth.
Basement Water Problems Long Island Warning Signs
Basement Waterproofing – Waterproofing a Basement in Grand Ledge, MI – Cracks in Wet Basement Floor
Basement Wall-Floor Joint Leaks Basement Systems
What Causes Basement Leaks? How Basement Construction Leads to Basement Leaks
Basement Wall Cracks and Water Seepage – Questions about Repair – DoItYourself.com Community Forums
St Louis Drainage Solutions Basement Cracks
Related Posts: